Canberra Neurology offers Canberra’s first state-of-the-art EEG clinic with normal, long-term and ambulatory EEG testing available.
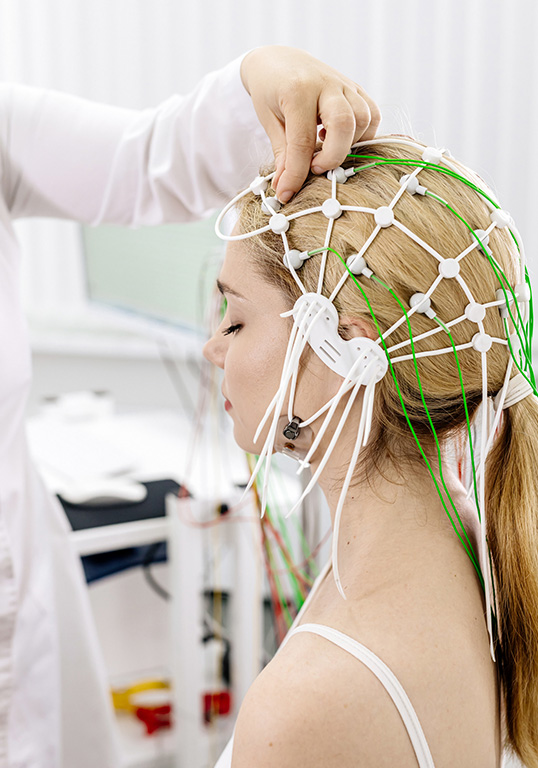
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a diagnostic test that measures electrical activity in the brain. This non-invasive procedure records brain wave patterns using small electrodes attached to the scalp.
These record the electrical impulses produced by brain cells (neurons) through small electrodes placed on the scalp. These impulses are displayed as wave patterns on a computer screen or paper, allowing healthcare professionals to analyse the brain’s electrical activity.
An EEG is painless and safe, and it provides valuable information about the functional state of the brain.
A Normal (Routine) Sleep Deprived EEG is a test that records brain activity after a period of reduced sleep. Electrodes are placed on the scalp to detect electrical signals from the brain. Sleep deprivation can increase the likelihood of detecting abnormal brain activity, particularly in conditions like epilepsy.
A Long-Term (Prolonged) Video EEG is a diagnostic test that continuously records brain activity and video over 3 hours or more. Electrodes are attached to the scalp, and the patient is monitored in a specialised setting. This test helps capture infrequent seizures or abnormal brain activity that may be missed on shorter tests.
An Ambulatory Video EEG is a portable test that records brain activity and video while the patient goes about normal daily activities, usually over 1 to 7 days. Electrodes are attached to the scalp and connected to a wearable recorder. This helps capture seizures or abnormal activity in a more natural setting.
The EEG procedure is straightforward and typically takes 30-minutes to an hour, although longer recordings may be required in some cases (ie: several hours or several days). The steps involved include:
EEG is used to diagnose and monitor a variety of neurological conditions, particularly those that involve abnormal brain activity. Some of the primary conditions include:
Overview:
Symptoms:
Treatment Options:
Overview:
Symptoms:
Treatment Options:


